
The invisible threat that could cripple your business is real, and it’s lurking in your inbox. Uncover the secrets to safeguard your company against relentless cyberattacks. Discover 11 crucial cybersecurity strategies that will safeguard your business from costly breaches and protect your reputation. Don’t be the next victim.
First Security Breach
Our office received an alarming after-hours call from a manufacturing firm desperate and in panic mode. The Company was very concern about emails being sent from their finance director to one of their customers asking for a change in payment method to a new bank account. The emails were also asking for a stop on all pending checks and redirected to the new bank account. These emails were sent to the customer by the finance director’s email account but not sent by their finance director! Panic mode ensued.
Wanting to help in quick order, we met with their CEO and in-house IT person to get a better understanding of the situation and to figure out what happened. In desperation, the manufacturing firm asked us to perform a security assessment to help find out what happened and for us to provide recommendations to avoid this issue in the future. During this process, we discovered that the finance director’s email account was compromised by a hacker that sent emails to their customers regarding open and current invoices. This was a planned, strategic attack that deliberately sent the appropriately designed email regarding payment at the correct time in the email communication thread (right email sent at the right time). Clearly the hacker had been watching the communication for the right time to strike! The customer was notified what had happened and that the new bank account was a fraud changed by the hacker.
We spent the next several days analyzing the manufacturing company’s email system to track who and where the compromise account was accessed from. We interviewed the accounting staff, IT staff members, and checked the email system logs. We found that the compromised account was being accessed using web mail from multiple locations (from different states, and outside the US).
As we continued to discuss the details with the designated IT person, we learned that this was the SECOND time their email was compromised (that they know of), and the CEO wanted us to help prevent this from happening again in the future.

Second Security Breach
In the second case, the IT director of a large construction firm contacted us about an email issue with their CEO. Emails were being sent out on behalf of the CEO using Outlook Contacts to send to all employees and customers.
This was all done without the CEO’s knowledge! The email subject line was, “Please review and sign your company Accounting Invoice 84XXX via DocuSign”. The company’s IT director asked us to work with his in-house IT team and perform a security review to determine the cause of the compromise, and then make recommendations going forward.
These types of scenarios are not at all too uncommon,

92.4% of cyber-attacks are delivered via email (Verizon: 2018 Data Breach Investigations Report)[1].
“Human error is one of the biggest weaknesses exploited by cybercriminals, and 17% of the tactics they utilize come in the form of social attacks”.
In both cases, the hacker (via email account) was impersonating the Finance Director and CEO. The hacker used their email accounts to send out messages to customers asking them to pay invoices or transfer money.
Both the finance director and CEO did not have any malicious intent when clicking on the email that allowed the compromise to happen, but they were the unknowing “gateway” that permitted the hacker into the company network. With the right amount of social engineering, exploiting on these individual’s good nature, they were tricked or coerced into clicking on a link in an email and enabled the hacker to gain access to your corporate email systems and send personal messages to all their contacts. As the result these incidents, it damages the business reputation, and costs the business money and downtime to investigate and report to law enforcement. To prevent future incidents like this, all users (CEO, Finance Director, and employees) must be part of the solution to understand the important of cyber-security, how they help to protect the company data, and report any security issues right away.
Things have changed, cyber-attacks are way up since people have started working from home in 2020. According to IBM, the average time to identify and contain a breach in 2020 was 280 days and average total cost of a data breach is $3.86 Million.[2] This means a company has been compromised and the hacker has been watching them, logging activities, and waiting for the right opportunity to strike. People working from home often have fewer security defenses on their home network that they would have in the office. For example, many people are using a wireless network that is not protected or network without any firewall at home. Some employees are also using home computers for company business that do not have the latest antivirus or the most recent security updates (for both the operating system and software applications).
We would like to share a few ways to help protect you and your company from a cyberattack:
1. Security Training and Policies– Provide training to all your employees and contractors about data security, email attacks, and your company policies and procedures. Employees need to understand how important cybersecurity is to your company and your bottom line. They need to know how they can protect against phishing scams, phone scams, and how-to report a security incident.
[1] https://enterprise.verizon.com/en-gb/resources/reports/dbir/2018/
[2] https://www.ibm.com/security/data-breach
2. Encrypt Sensitive Files – Most likely, your computer and company server have sensitive data stored or saved on them. You would want to encrypt specific data or files that would still allow the appropriate company personnel access to the information. For the computer, you could encrypt the entire disk drive using Windows 10 BitLocker and MacOS. However, it would be better to encrypt only the files and folders where the sensitive data is stored. This will require specialize software that your IT professional can help you with.
3. Encrypt Sensitive Email Messages – if you send email messages that contain sensitive information like social security, credit card, and personally identifiable information (PII), encrypt the email. Companies can setup secure email in Office 365, Google Workplace (G-suite) and use their party software like ZixMail.
4. Controlled Access / Least Privilege Policy—your company have sensitive information and customer data, restrict access to only the individuals that needs the data to perform their job. Segment the data into different job roles or department and give only access to employees or contractors that must-have access. For example, setup different network share and security permission for Finance, Engineering, and Operations departments. Don’t give CEO/President account or Office Manager full Administrator permission to server or email systems; setup a separate service account if one is required to manage risk. Have policies and procedures to remove access after an employee is terminated.
5. Anti-Virus– Have anti-virus and anti-malware installed and running in a pro-active mode on your computer with recommended daily updates and scans. Use the latest next-gen antivirus advanced endpoint detection and response software.
6. Standard Password with Multi-Factor Authentication– Use Strong passwords that have 12-characters or more along with multi-factor authentication for email, applications, and network access. This security feature verifies “is it you” trying to access my account? For example, set up two-step authentication for your Office 365 or Google G-mail when you logon to access email or on-line storage such as OneDrive or G-drive. Two-step authentication is what your online banking systems use – you must enter a username, password and one-time code or text message code to complete the log on process.
6A. For Microsoft Office 365, here is the step-by-step Setup Instruction Guide for MFA or 2-step verification:
6B. For Google Apps or G-suite, here is the step-by-step Setup Instruction Guide for 2-Step verification:
https://support.google.com/a/answer/9176657?hl=en
7. Use a Password Manager– to create a strong password and save you time. In today’s busy world, we have so many passwords to remember for various accounts it is almost impossible to keep track of all of them. It is recommended that you use a professional password manager to help you create a strong and unique password for each account. For example, we have setup Last Pass, Keeper Security, and RoboForm for many of our customers. Using your browser password manager is okay for individual home use, but it does not provide full management, security, and reporting compared to third-party business password manager.
8. Be Careful When Using Public WiFi for Conducting your Business– Using public WiFi or hotspots at Starbucks or Hotels can be a very risky activity because you do not control the wireless device or the Internet you are going through. Hackers can be monitoring the wireless connection and capturing the information.
You should consider the following safeguards when using Public WiFi…..
- Use a VPN, SSL Connection and Turn Off Sharing on your computer if you must use public WiFi.
- Use the Company’s latest VPN client version for SonicWALL SSL VPN or Global VPN, Fortinet, and Cisco VPN client to connect to your office.
- When using a web browser, confirm you are using the security protocol SSLconnection. For example, in a Chrome web browser, it will have an SSL lock pad icon on display in the URL bar (see snapshot listed below)
When you go https://support.google.com/a/answer/9176657?hl=en
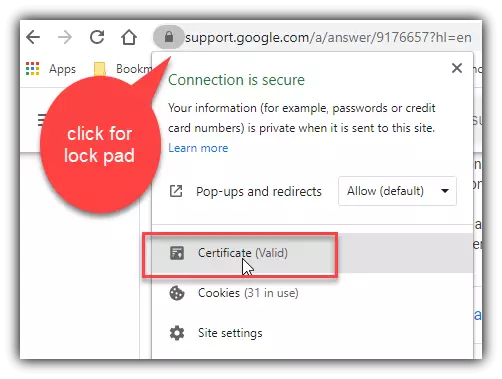
9. Update Software and Security Patch Promptly – promptly updating Windows 10 or MacOS and applications to protect against known vulnerabilities. Use only the vendor supported release version of your application software. For example, do not use an old version of Windows 7, Microsoft Office, Antivirus or QuickBooks that are no longer supported or out of warranty by the software vendors. They will not have the latest security updates/patches available anymore and hackers are looking for ways to exploit these weaknesses.
10. Online Web Meeting Tools – many people are using online web conferences to host video conferences, chat, and text messaging. It is very important to be aware of the ways these tools may impact your digital privacy and security. Free products from Zoom, Skype, Meet and Slack may collect and store your information and retain messages. Read the vendor privacy rules to understand how they track users and what is stored. You should consider using your company web meeting tools so you can control your own privacy. For example, if you have Office 365 or Google G-suite or Zoom, configure corporate-wide security policies such as requiring meeting password and waiting room or sharing of information.
11. Backup and Check Your Data – backup your files, email, and online applications, but test the backup regularly (monthly or quarterly). Your data and customer information are the most valuable things to you and your company. It is important to automate the process of backing up your data to the Cloud and to also save a backup data copy locally for easy recovery. You should also have data loss prevention policies to protect sensitive information from getting sent out outside your company or uploaded to online storage. If you do not have a good backup solution for backing up your workstation, you can use OneDrive for Business, Google Drive Sync, and Windows backup to save a copy to an external drive. Test the backup to ensure it works!
CONCLUSION
Network Security is not a one-time event, do not treat it like the saying, “Set It and Forget It”. With having a more mobile workforce, anywhere access to company email and applications, employees are being targeted with phishing email or social media. Thus, educating your employees about cyber-security along with on-going monitoring of your network security, is critical to prevent a data breach and to avoid your company’s reputation from being tarnished in the news or in any other way.
If you would like to learn how we can help, including managed cyber-security and proactive IT services, and employee security awareness training, download a free audiobook how to “Avoid these Five Deadly Computer Disasters, and Save Your Business” or schedule a free strategy call at http://esudo.com/booking.

The Importance of Keeping Your Chrome Browser Updated: A Critical Aspect of Cybersecurity
Update Chrome in 1 minute to keep you safe online...
Read MoreIT Infrastructure Considerations for California Law Firms: Scaling for Growth and Reliability
The COVID-19 pandemic has fundamentally altered operational dynamics worldwide, compelling...
Read MoreCollaboration Tools for Bay Area Legal Teams: Enhancing Communication and Workflow Efficiency
In the fast-paced environment of law firms, corporate legal departments,...
Read MoreCyber Insurance Application Filing Guide for your Business
What You Need To Know About Filling Your Cyber Insurance...
Read More




